
Asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral, has been valued for its remarkable properties throughout history.
Its ability to resist heat, fire, and corrosion, coupled with its durability, made it a sought-after material for various industrial and construction applications.
But exactly how is asbestos made?
From ancient times to the modern era, asbestos has been woven into fabrics, mixed into building materials, and utilised in insulation and fireproofing.
However, despite its widespread use, the manufacturing process of asbestos and its associated hazards has outlawed its use in the vast majority of the world.
Table of Contents
How is Asbestos Made?
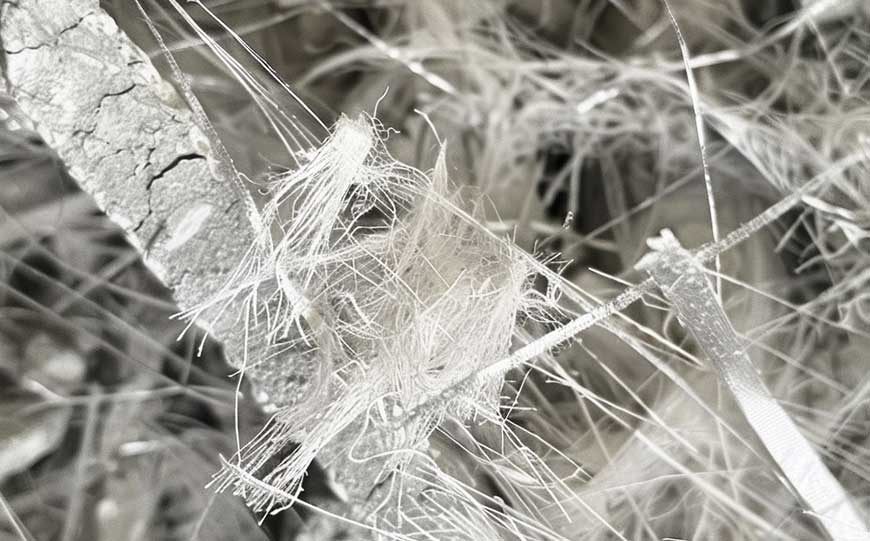

Asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral, is not man-made. The production of asbestos fibre begins with the extraction of asbestos-containing rocks from the earth.
These rocks undergo a process of crushing and milling to release the asbestos fibres contained within them.
Once extracted, these fibres are collected and processed for use in various industrial and construction applications.
Asbestos fibres are known for their durability, heat resistance, and insulating properties. Because of these qualities, they have been incorporated into a wide range of products, including lagging, cement, sprayed coatings, insulation, and protective gear like gloves and blankets.
This natural material’s transformation into various products underscores its former widespread usage across several industries.
Despite its beneficial properties, asbestos poses significant health risks, and was outlawed in the UK in 1999.
How is Asbestos Lagging Made?

Asbestos lagging, a prevalent form of asbestos insulation, was manufactured through a meticulous process.
Initially, asbestos fibres are extracted from asbestos-containing rocks through crushing and milling.
Subsequently, these fibres are combined with a binding agent to form a paste-like substance.
This paste is then meticulously applied onto pipes, boilers, or other surfaces requiring insulation against heat and fire.
The application process of asbestos lagging demands precision and expertise to ensure proper coverage and adherence to surfaces.
Once applied, the lagging provided effective insulation, safeguarding against extreme temperatures and potential fire hazards.
How is Asbestos Cement Made?
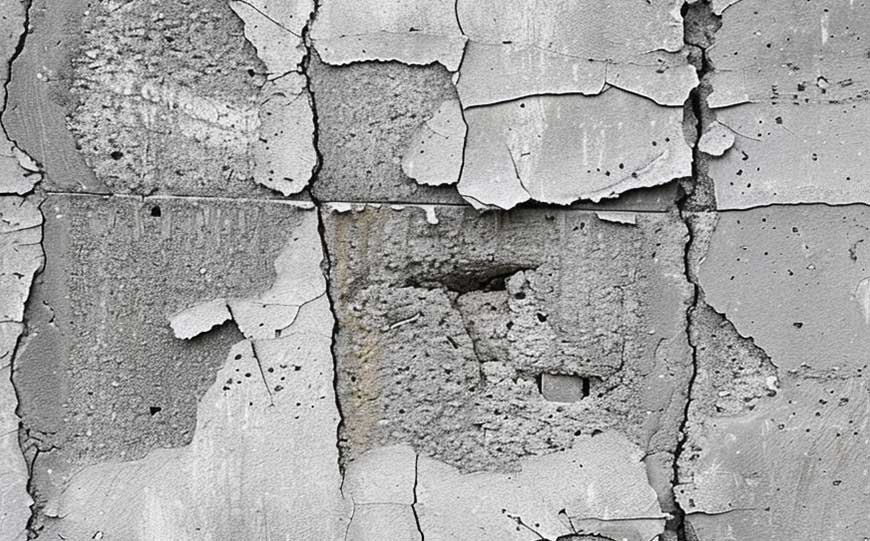

Asbestos cement was a widely used construction material renowned for its durability and fire resistance.
It was produced through a meticulous manufacturing process.
Asbestos fibres are combined with Portland cement, a binding agent known for its strength and stability.
The asbestos fibre and cement mixture is thoroughly blended to ensure uniform distribution of fibres within the cement matrix.
Once mixed, the resulting slurry is moulded into sheets, pipes, or other desired shapes using specialised equipment.
The moulded products are then allowed to cure and harden, resulting in sturdy and resilient asbestos cement materials.
Asbestos cement found applications in various construction projects, including roofing, siding, and piping, due to its ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions and resist corrosion and fire.
How are Asbestos Sprayed Coatings Made?

Asbestos sprayed coatings, known for their fire-resistant properties, were manufactured through a thorough process.
Asbestos fibres are then mixed with a binding agent and water to create a slurry-like consistency.
The slurry is carefully sprayed onto surfaces using specialised equipment, such as spray guns or nozzles.
As the sprayed coating adheres to the surface, it forms a protective layer that acts as insulation against heat and fire.
The application process of asbestos sprayed coatings required skill and precision to ensure even coverage and proper adhesion.
Once applied, the coating forms a durable barrier that can withstand high temperatures and provide effective fire protection.
How is Asbestos Insulation Made?

Asbestos insulation was valued for its heat resistance and insulating properties.
Asbestos fibres are combined with other insulating materials, such as vermiculite or cellulose, to enhance their thermal properties.
The mixture is carefully blended to ensure uniform distribution of asbestos fibres throughout the insulation material.
Once mixed, the resulting mixture is formed into sheets, blocks, or other desired shapes using specialised equipment.
The formed insulation products are then allowed to cure and harden, resulting in durable and effective insulation materials that can withstand high temperatures and provide efficient thermal insulation.
How are Asbestos Gloves and Blankets Made?
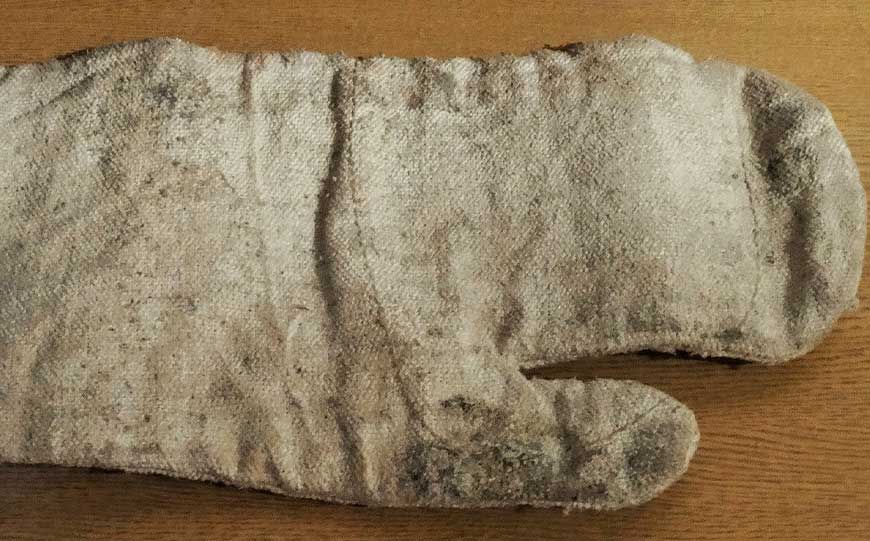

Asbestos gloves and blankets, known for their heat resistance and protective qualities, were manufactured by having asbestos fibres spun into yarn, which is used to weave fabric.
The woven asbestos fabric is the primary material for making gloves and blankets.
For gloves, the asbestos fabric is cut and sewn into the desired glove shape.
The seams are reinforced with additional stitching or binding to ensure durability and protection against heat and fire.
For blankets, large sections of asbestos fabric are cut to the required size.
The edges are often hemmed or bound to prevent fraying and to provide a finished appearance.
The asbestos blankets are then inspected to ensure uniformity and effectiveness in providing thermal protection.
Why is Asbestos Dangerous?
Asbestos, while it was highly useful in various industrial applications, poses significant health risks.
The primary danger stems from its fibrous nature, which can lead to severe respiratory diseases when inhaled.
Inhalation of Asbestos Fibres
Asbestos is dangerous because its fibres can become airborne when materials containing it are disturbed.
This happens during construction, demolition, or even simple maintenance activities.
Once airborne, these microscopic fibres can be easily inhaled, lodging themselves in the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system.
Respiratory Diseases
Prolonged exposure to asbestos fibres can cause several serious diseases:
Asbestosis
This chronic lung disease is caused by inhaling asbestos fibres, leading to lung tissue scarring.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, persistent cough, and chest tightness.
Asbestosis can severely impair lung function and is often irreversible.
Lung Cancer
Exposure to asbestos significantly increases the risk of lung cancer, especially among smokers.
The latency period for lung cancer development can be decades, making it a hidden but deadly threat.
Mesothelioma
This rare and aggressive cancer affects the lining of the lungs (pleura) or the abdomen (peritoneum).
Mesothelioma is almost exclusively caused by asbestos exposure and has a very poor prognosis, often proving fatal within months of diagnosis.
Other Health Risks
Besides respiratory diseases, asbestos exposure can also lead to other health problems.
For example, it can cause pleural plaques, which are thickened patches on the pleura, and pleural effusions, which are fluid buildups in the chest cavity.
Both conditions can cause significant discomfort and health complications.
Long Latency Period
One of the most insidious aspects of asbestos exposure is the long latency period.
Symptoms of asbestos-related diseases may not appear until 20 to 50 years after exposure.
This delayed onset means that individuals exposed to asbestos may not realise the severity of their condition until it is too late for effective treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding how asbestos is made and its potential dangers is crucial for protecting public health and safety.
Asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral, had been prized for its desirable properties, such as heat resistance and durability, making it a popular choice for various construction materials.
However, its use must be carefully managed to prevent exposure and minimise risks.
Asbestos fibres, when disturbed, can become airborne and pose severe health risks.
To prevent harm to workers and the general population, asbestos-containing materials should be properly handled, removed, and disposed of by trained professionals following strict safety protocols.
Since 1999, it has been essential to promote safer alternatives and practices,
By prioritising safety and awareness, we can mitigate the dangers associated with asbestos and safeguard public health.
For any and all asbestos related issues, get in touch with us here at KD Asbestos.