
Anthophyllite is a rare mineral belonging to the amphibole group.
It is primarily composed of magnesium and iron silicate, forming under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in metamorphic rocks.
Anthophyllite has a fibrous structure, and is a form of asbestos.
Understanding anthophyllite is essential for both geological studies and public health.
This article will explore what anthophyllite is, its appearance, uses, locations, identification methods, and dangers.
Table of Contents
What is Anthophyllite?
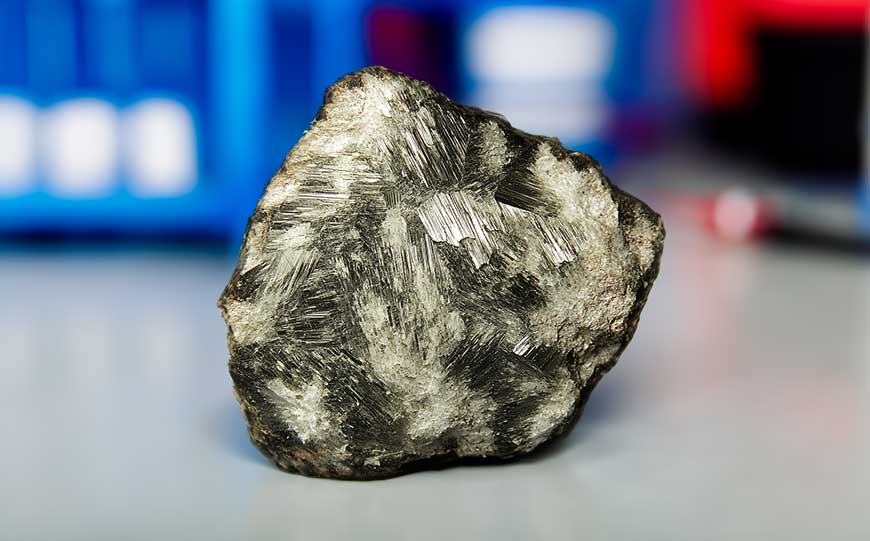

Anthophyllite is a rare mineral that belongs to the amphibole group.
Its chemical composition primarily includes magnesium and iron silicate, forming under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in metamorphic rocks.
Its chemical formula is:
(Mg,Fe)7Si8O22(OH)2.
It forms under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in metamorphic rocks.
This makes it a common component of certain geological formations.
Anthophyllite is often associated with other minerals like talc, pyroxene, and biotite.
It has a fibrous structure and is one of the many different types of asbestos.
This is important, as it has been linked to health risks.
What Does Anthophyllite Look Like?
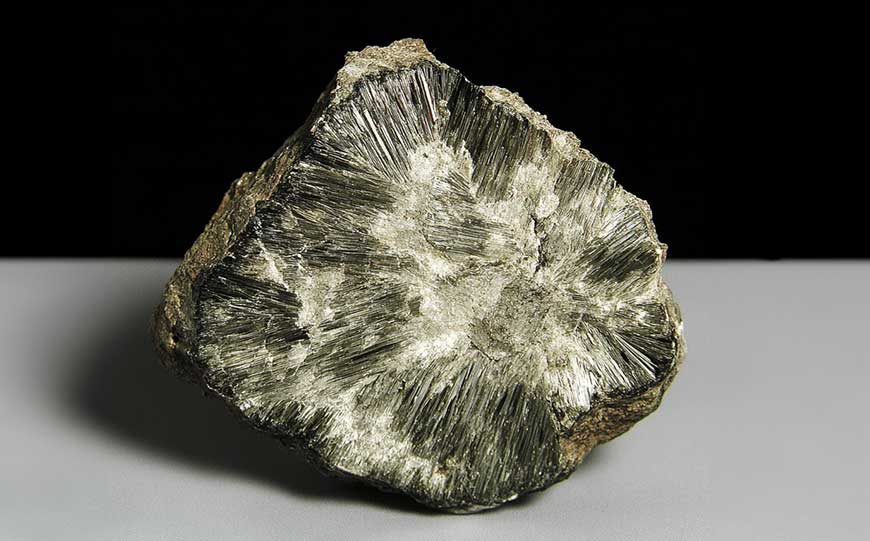

Anthophyllite typically appears as a fibrous mineral with colours ranging from brown to green or grey.
Its fibrous structure can give it a woolly or silky texture, making it visually distinct.
When viewed in hand samples, anthophyllite may display a shiny or dull finish, depending on its specific composition and treatment.
It often exhibits a unique pattern, breaking along its fibres.
The mineral’s hardness ranges from 5 to 6 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively durable.
When polished, anthophyllite can showcase a glassy or pearly lustre.
What was Anthophyllite Used For?

Anthophyllite has a range of historical uses, primarily due to its fibrous structure and heat-resistant properties.
Industrial Applications
Anthophyllite has historically been valued for its unique properties, particularly in industrial applications.
As a type of asbestos, it was prized for its heat resistance and fibrous structure.
This made it suitable for various insulation materials in buildings, industrial equipment, and piping systems.
Construction Materials
In construction, anthophyllite was commonly incorporated into fireproofing products.
It was used in roofing materials, flooring tiles, and plaster, helping to enhance fire resistance and durability.
Its ability to withstand high temperatures made it an essential component in protective coatings and sealants as well.
Automotive Uses
In the automotive industry, anthophyllite found use in brake linings and gaskets.
Its high heat resistance was critical in these applications, where extreme temperatures and friction were common.
This made anthophyllite a reliable material for ensuring safety and performance in vehicles.
Mineral Collectors and Geologists
Beyond industrial uses, anthophyllite is also of interest to mineral collectors and geologists.
Its unique fibrous appearance and rarity make it a sought-after specimen for display and study.
Where is Anthophyllite Found?

Anthophyllite is primarily found in metamorphic rocks that form under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
These conditions lead to the transformation of pre-existing rocks into new mineral compositions, making anthophyllite a common component in such geological formations.
Its presence indicates specific environmental conditions during the rock formation process.
Significant deposits of anthophyllite exist in several regions around the world.
USA
In the United States, notable locations include Vermont and North Carolina.
Here, anthophyllite is found within metamorphosed ultramafic rocks, which are rich in magnesium and iron.
These states have become key sites for anthophyllite research and mining.
Finland
Finland is another country with extensive anthophyllite deposits.
In this region, it occurs within Precambrian metamorphic formations, showcasing its long geological history.
The mineral’s presence in Finland contributes to the understanding of regional geology and metamorphic processes.
Australia
In Australia, anthophyllite can be located within gneiss and schist rocks, both of which are typical of metamorphic environments.
These geological settings often contain a variety of minerals, contributing to anthophyllite’s unique formation conditions and distribution.
Mineral Associations
Anthophyllite is frequently found alongside other minerals, such as talc, pyroxene, and biotite.
These associations provide insights into the geological processes that led to the formation of anthophyllite and its occurrence in various rock types.
Understanding these relationships helps geologists interpret the history and evolution of the Earth’s crust in different regions.
How to Identify Anthophyllite Asbestos

Identifying anthophyllite asbestos requires careful examination due to its fibrous structure and similarities with other asbestos types.
Microscopic Analysis
One of the most reliable methods for identifying anthophyllite asbestos is through microscopic analysis.
Techniques such as polarised light microscopy (PLM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can provide detailed insights into the mineral’s structure and composition.
In PLM, specific optical properties of anthophyllite, such as its refractive index and birefringence, can help distinguish it from other asbestos types.
SEM can reveal the fibrous morphology and surface features unique to anthophyllite.
Fibrous Structure
Anthophyllite asbestos is characterised by its distinct fibrous structure.
Asbestos fibres are typically thin and can be long, often giving a silky or woolly appearance.
This fibrous nature is a key identifier, as it differentiates anthophyllite from non-asbestos minerals.
When examining samples, look for a fibrous texture that can be easily separated into fine strands.
Colour Variation
Anthophyllite is commonly found in shades of brown, green, or grey.
The colour may vary depending on its specific mineral composition.
A visual inspection of the material can provide preliminary clues, but colour alone should not be the sole factor in identification, as other asbestos types may exhibit similar hues.
Asbestos Testing Kits
For non-experts, asbestos testing kits can offer a convenient way to test for the presence of anthophyllite.
These kits usually include sample collection tools and instructions.
However, they may not always provide conclusive results specific to anthophyllite.
Professional Inspection
For accurate identification, consulting a professional inspector is crucial, such as us here at KD Asbestos.
Experts can perform laboratory analyses to confirm the presence of anthophyllite asbestos and ensure proper safety protocols are followed.
What are the Dangers of Anthophyllite?
Anthophyllite poses significant health risks, primarily due to its classification as a type of asbestos.
When disturbed, anthophyllite can release tiny fibres into the air, leading to asbestos exposure.
Inhalation of these fibres can lead to serious health issues, making it critical to understand the dangers associated with this mineral.
Respiratory Diseases
One of the primary dangers of anthophyllite exposure is the development of respiratory diseases.
Inhaled asbestos fibres can become lodged in lung tissue, leading to conditions such as asbestosis.
This chronic lung disease causes inflammation and scarring of lung tissue, resulting in breathing difficulties and reduced lung function over time.
Lung Cancer
Long-term exposure to anthophyllite asbestos significantly increases the risk of lung cancer.
The risk is compounded for individuals who smoke, as the combination of smoking and asbestos exposure greatly heightens the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
Symptoms may not appear for many years, making early detection challenging.
Mesothelioma
Another severe health risk associated with anthophyllite is mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs and abdomen.
Mesothelioma is almost exclusively linked to asbestos exposure, and its prognosis is often poor.
The latency period for this disease can be long, with symptoms emerging decades after exposure.
Regulatory Concerns
Due to these health risks, the use of anthophyllite asbestos is highly regulated in many countries.
Buildings and materials containing this mineral must be handled with care to prevent fibre release.
Proper safety protocols, including personal protective equipment (PPE) and professional inspections, are essential for anyone working with or around materials that may contain anthophyllite.
Conclusion
You should now have more of an understanding of Anthophyllite.
Anthophyllite is a rare mineral with a complex history.
It is primarily known for its fibrous structure and as a form of asbestos.
While it has valuable properties for industrial applications, it poses serious health risks.
Understanding anthophyllite’s characteristics and dangers is essential for safe handling and use.
Responsible management of materials containing anthophyllite are incredibly important.
For more information, or for help with your asbestos-related needs, get in contact with us here at KD Asbestos.